The cost of fraud
Published: 30 Apr 2022
We’ve all seen the breaking news section where data breaches from huge organizations have spread across the media. When a person has their credit card in their possession, they’re responsible for that physical card, but what happens when the card number is given to someone else? Credit card payments. We all know what these are, whether we need them for our businesses to collect money or as a consumer to buy something we need.
Using a credit card seems so simple. It takes a second or two and most people don't think twice about what's happening to make it work, even the merchant. But the process is actually quite complex, and, as everyone has seen over the past few years, having all those credit card numbers floating around in the world can result in some very negative results, like data breaches and fraudulent transactions.
I'm going to explain the differences between the entities involved in the process and what their interactions are with the other pieces of the puzzle. Each individual or organization has their own responsibility to protect credit card data, and most of those are required to do so because of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards, also known as PCI Compliance.
As we covered in the previous lecture, we have the consumer, the merchant or store, the merchant's payment processor, the merchant's bank and the consumer's bank, and then the credit card networks. So let’s have a closer look at what is on a card?
There's the primary account number, or PAN, which is the number on the card identifying the associated account number. It's usually 15 or 16 digits long. Then there’s the expiration date, and the Card Verification Value, or CVV number, also known as CSE, CVV2, or CVC2. It's three or four digits, it’s usually at the back of the card, but it can be on the front if the card is an American Express.
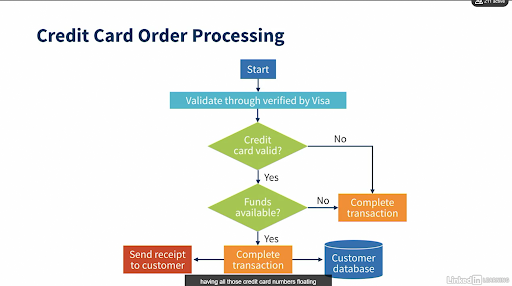
Then there’s the magnetic strip that contains all this information; the PAN, the cardholder name, expiration date and other key pieces of information about the institution that issued the card. If thieves have your PAN, they can create a fake physical card with the data on the magnetic strip and take it to physical stores to buy high value items they can sell. Finally, we have the chips commonly seen on current credit cards.
If you're involved with any part of the workflow, you will learn where the greatest risks can be found as well as some basic changes you can make to protect your individual card number as well as changes that your organization may need to look into, if it takes credit or debit cards for payment.
Sometimes people think that being a victim of fraud is an isolated case and the result of a genuine "mistake". However, more often than not these scams are done over and over again with numerous victims.
Many factors could be accounted for the growth of the iGaming industry. Technological advance means that the games are constantly evolving and improving. All kinds of betting services are offered with better visual and audio design which naturally attract more customers.
It’s inevitable. Some fraudulent orders will slip through your systems. Which is why fraud prevention systems are so important.
Today’s technological advancements have made online fraud a prevalent business. In 2018, transaction fraud losses incurred by US merchants and card issuers hit $9.1 billion. Doing nothing about fraud can be catastrophic for organizations and implementing the right fraud prevention process is critical.
One of the greatest concerns surrounding the introduction of real-time payments is the heightened risk of fraud—a risk that is all too real. When the UK launched its Faster Payments system in 2008, fraud losses from online banking rose by almost 300 percent— from £22.6M in 2007 to £59.7M in 2009. The irony is that some of the key benefits of technological advances and real-time payments are also their main weaknesses.
Online merchants know very well that fraud costs them in many ways — in chargebacks, in false positives, in the friction that’s introduced at checkout that can cost a sale. When it comes to fraud, the cost of doing nothing appears to be quite a bit costlier — at least in the long run. The actual cost of fraud losses are $2.27 for each $1 of eCommerce fraud. For mobile that cost is a bit lower, with the actual fraud cost for every $1 of mobile commerce fraud costing $2.08.
And that's not a risk merchants can afford to take. And as it turns out, they also can't afford to do nothing when it comes to fraud mitigation, as doing nothing appears to cost more than actually doing something. At least that's what the data show.
Want to learn more? Enroll in our Risk, Payments and Fraud course on Udemy by clicking here
.




